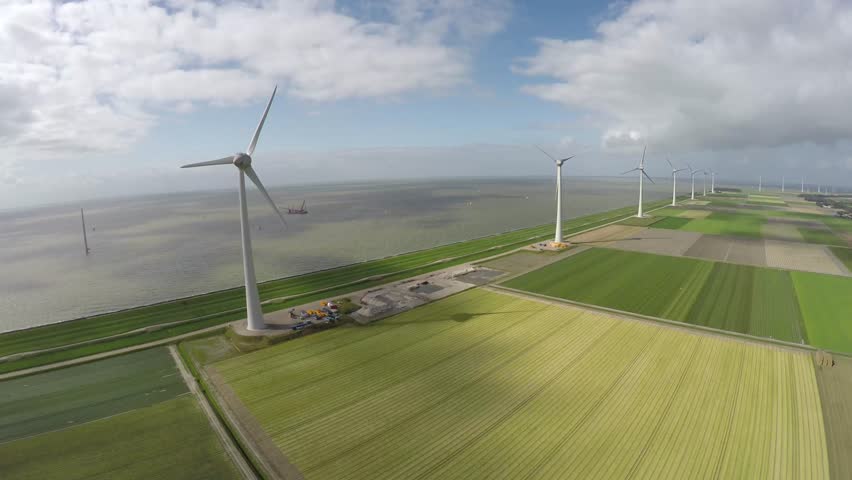
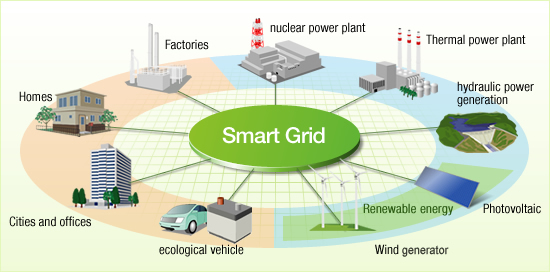
The Smart Grids Programme is one of the six flagships programmes within the South African National Energy Development Institution (SANEDI).  Smart Grids programme is focused on the introduction of various concepts of Smart Grids within the South African Electricity Distribution Industry (EDI).
Smart Grids programme is focused on the introduction of various concepts of Smart Grids within the South African Electricity Distribution Industry (EDI).
SANEDI smart grids team’s mandate is to integrate and optimise distributed energy resources to achieve a more efficient and reliable grid, enable active participation of consumers with more environmental constraints.
The Smart Grid Programme addresses the Government’s Medium Term Strategic Framework (MTSF) objectives of Energy Transformation and Service Delivery. With regards to Energy Transformation, technology innovation is used as an enabler for change. The introduction of Smart Grid technology is a key enabler for South Africa to achieve its energy mix. Without smart grids large scale integration is impossible. This allows South Africa to meet its climate change objectives at municipal level. With regards, to Service Delivery, Smart Grid Technology is enabling the use of integrated systems and processes in the municipal environment thus enabling efficiencies and effectiveness not seen before in the municipal environment.